Optimizing the model
Description
Optimize the model before you calculate it in case of insufficient data, an inadequate calculation period or results that are not satisfactory for other reasons. You can edit a saved model.
-
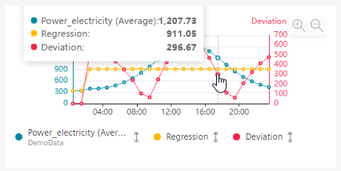
To show details on a data point, move the cursor over the graphic.
-
To show or hide a parameter, click it below the preview.
-
To zoom into the area, move the mouse pointer over the area while keeping the mouse button pressed.
The following is displayed in addition to the visualization preview:
-
Formula

The formula describes the relationship of the output parameter y to the input parameters x1, x2, etc.
The formula cannot be edited.
-
Correlation coefficient
The correlation coefficient is the quality measure for the model: How well does the model describe the actual data? The lower the value of the correlation coefficient, the less trustworthy the model.
The correlation coefficient can range from 0% to 100%. The higher the value, the better the model.
If the correlation coefficient is < 60%, adjust the model. Access a larger data volume or select different parameters.
-
F-test
Indicates the significance of the model: Is the calculated model better than a random model?
The greater the value of the F-test, the better the model. If the value is displayed in red, adjust the model. Select other parameters or a longer calculation period.
When you move the mouse pointer over the graphic, the details of individual data points are displayed in the tooltip.
To zoom in on the time range, move the mouse pointer above the desired area of the graphic while pressing the left mouse button.
Click on "Zoom out" to gradually show the view for a longer time range.
Click on "Reset zoom" to restore the original display.
Procedure
To optimize a model, follow these steps:
-
Use variables or KPIs as output parameters and input parameters for which data is available without gaps in the calculation time range.
-
If necessary, remove input parameters with insufficient data quality.
-
Select a calculation period during which the data quality is better.
-
Change the spike correction to mitigate the effect of extreme variable values.
-
Recalculate the formula after each change.
-
When you have achieved an acceptable result, save the model.