Introduction to KPI calculations
Description
The abbreviation KPI stands for Key Performance Indicator.
A KPI type is a formula consisting of operands, constants and operators. The definition and calculation of KPI types are plant-specific.
Example of a KPI type:
-
Quality rate = Good Items / Total Items * 100
A KPI instance can be created either during the widget configuration in the "Parameter" step, or in the parameter list on the asset. The KPI instance can
-
be derived from a KPI type (typed)
-
or can be created typeless.
KPI types can be instantiated multiple times. When you make changes to the KPI type, these changes are also implemented in all KPI instances.
Automatically created KPI instances
KPI instances are created automatically as soon as the configuration for an automatically generated dashboard, e.g. an OEE analysis, has been made on an asset.
For automatically created KPI instances, you can define limits that trigger a notification when these limits are exceeded or not reached. The green check mark in the "Notifications activated" column shows that a notification has already been configured. More information on the configuration of notifications can be found here: "Activate notifications" for variables with numerical data type and KPI instances.
In the parameter list, you can identify the automatically created KPI instances by the blue icon.
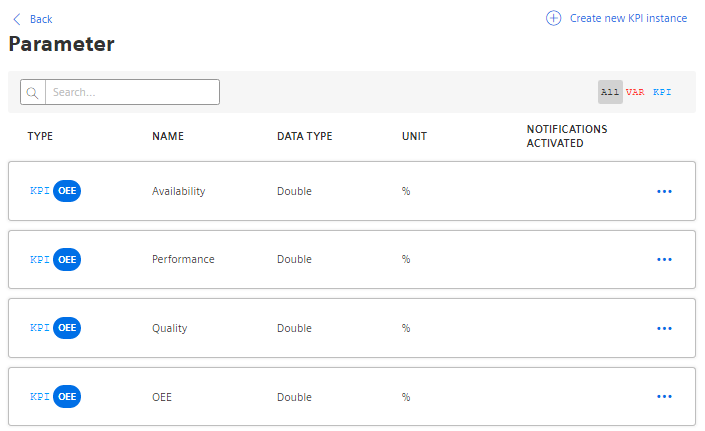
Structure of a KPI instance
The KPI instance is created as follows:
-
Instantiate a KPI type including linked variables or KPI instances (typed; multiple use is possible)
- or -
Create a KPI instance directly and link it to variables or KPI instances (typeless).
Each KPI instance must be assigned to an asset, but variables from other assets can also be linked to the KPI instance.
The following figure shows the individual components that make up a KPI instance.
-
Operands serve as placeholders that are later filled with actual values from the variables or KPI instances.
-
Constants can only contain numerical values
-
Operators
The following diagram shows the structure of the KPI type/instance concept:
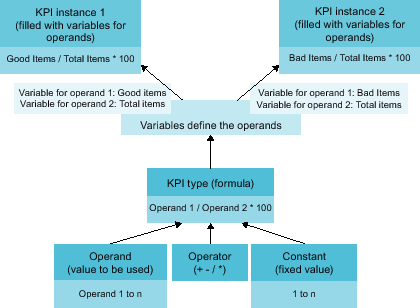
Operands
Operands serve as placeholders that are later filled with actual values from the variables. They are created when creating a KPI type and defined during the instantiation of the KPI type. Operands must not contain spaces, mathematical symbols, or numbers at the beginning of the operand name. They can be moved and copied.
NOTE
The KPIs are saved in a cache. If values in the platform were overwritten in the past (except for the current and last hour), it may take up to one hour before you can see the data or KPIs and aggregations based on them.