Using a9s RabbitMQ¶
This section describes how developers use a9s RabbitMQ.
Use a9s RabbitMQ with an App¶
To use a9s RabbitMQ with an application, create a service instance and bind the service instance to your application. For more information on managing service instances, see Managing Service Instances with the cf CLI.
View the a9s RabbitMQ Service¶
After the tile is installed, you can see the rabbitmq and its service plans appear in your PCF marketplace. Run cf marketplace to see the service listing:
$ cf marketplace
Getting services from marketplace in org test / space test as admin...
OK
service plans description
rabbitmq36 rabbitmq-xs, rabbitmq-m, This is the anynines rabbitmq 36 service.
Create a Service Instance¶
To provision a RabbitMQ database, run cf create-service. For example:
cf create-service rabbitmq36 rabbitmq-xs my-rabbitmq-service
Depending on your infrastructure and service broker utilization, it might take several minutes to create the service instance.
Run the cf services command to view the creation status. This command displays a list of all your service instances. To view the status of a specific service instance, run cf service NAME-OF-YOUR-SERVICE.
Bind an Application to a Service Instance¶
After your database is created, run cf bind-service to bind the service to your application:
cf bind-service rabbitmq-app my-rabbitmq-service
Restage or Restart Your Application¶
To enable your application to access the service instance, run cf restage or cf restart to restage or restart your app.
Obtain Service Instance Access Credentials¶
After a service instance is bound to an application, the credentials of your RabbitMQ database are stored in the environment variables of the application. Run cf env APP-NAME to display the environment variables.
You can find the credentials in the VCAP_SERVICES key.
$ cf env rabbitmq-app
Getting env variables for app rabbitmq-app in org test / space test as admin...
OK
System-Provided:
{
"VCAP_SERVICES": {
"rabbitmq": [
{
"credentials": {
"default_database": "d22906",
"hosts": [
"EXAMPLE-HOST"
],
"password": "EXAMPLE-PASSWORD",
"uri": "EXAMPLE-URI",
"username": "EXAMPLE-USERNAME"
},
"label": "rabbitmq",
"name": "my-rabbitmq-service",
"plan": "rabbitmq-xs",
"tags": [
"nosql",
"database",
"document store",
"eventual consistent"
]
}
]
}
}
...
You can use the host, username and password values to connect to your database with a RabbitMQ client.
Delete an a9s RabbitMQ Service Instance¶
Warning
Before deleting a service instance, you must backup data stored in your database. This operation cannot be undone and all the data is lost when the service is deleted.
Before you can delete a service instance, you must unbind it from all apps.
List Available Services¶
Run cf services to list your available services.
$ cf services
Getting services in org test / space test as admin...
OK
name service plan bound apps last operation
my-rabbitmq-service rabbitmq36 rabbitmq-xs rabbitmq-app create succeeded
This example shows that my-rabbitmq-service is bound to the rabbitmq-app application.
Unbind a Service Instance¶
Run cf unbind-service to unbind the service instance from your app.
cf unbind-service rabbitmq-app my-rabbitmq-service
Delete a Service Instance¶
After unbinding the service, it is no longer bound to an application. Run cf delete-service to delete the service:
cf delete-service my-rabbitmq-service
It may take several minutes to delete the service. Deleting a service deprovisions the corresponding infrastructure resources. Run the cf services command to view the deletion status.
Upgrade the Service Instance to another Service Plan¶
Once created, you can upgrade your service instance to another larger service plan. A larger service plan provides more CPU, RAM and/or storage. The plans also differ in availability. For more information, refer to Service Plans.
cf update-service my-rabbitmq-service -p a-bigger-plan
Here are the plans you can upgrade to depending on the one you are currently using:
| From / To | xs | s10 | m50 | s10_ha | m | m150_ha |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| xs | - | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| s10 | no | - | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| m50 | no | no | - | no | yes | yes |
| s10_ha | no | no | no | - | yes | yes |
| m | no | no | no | no | - | yes |
| m150_ha | no | no | no | no | no | - |
The left column shows your current plan and the first row shows the target plan.
Example:
If your current plan is rabbitmq-s10, it's possible to upgrade to rabbitmq-m50, rabbitmq-s10_ha, rabbitmq-m and rabbitmq-m150_ha, but it is not possible to upgrade to rabbitmq-xs.
Add a Graphite Endpoint¶
If you want to monitor your service with Graphite, you can set an endpoint to where to information will be sent with the cf update-service command. This command expects the -c flag and a JSON string containing the graphite and metrics_prefix keys. Depending on your graphite provider the metrics_prefix might require that each metrics must start with an API key in their name. You can also change the interval within the data is send to the endpoint. Do to this modify interval the default is 10s.
cf update-service my-rabbitmq-service -c '{ "graphite": ["yourspace.your-graphite-endpoint.com:12345"], "metrics_prefix": "your-api-key.my-cluster-rabbitmq", "interval": "5"}'
Info
Logging is only possible for service plans that have the Logging component enabled. For more information, refer to Service Plans.
You can delete the graphite endpoint settings by calling update-service with an empty array.
cf update-service my-rabbitmq-service -c '{ "graphite": []}'
Add a Syslog Endpoint¶
The cf update-service command used with the -c flag can let you stream your syslog to a third-party service. In this case, the command expects a JSON string containing the syslog key. You can also change the interval for the syslog with the same key than for the graphite endpoint interval.
cf update-service my-rabbitmq-service -c '{ "syslog": ["logs4.your-syslog-endpoint.com:54321"], "interval": "5" }'
Info
Logging is only possible for service plans that have the Logging component enabled. For more information, refer to Service Plans.
You can delete the syslog endpoint settings by calling update-service with an empty array.
cf update-service my-rabbitmq-service -c '{ "syslog": []}'
Cloud Foundry Application Security Groups¶
This section describes how to check whether a security group was created.
Each a9s Data Service will automatically create and update Cloud Foundry security groups in order to protected service instances to be accessed by applications not running in the same Cloud Foundry applications space. To get a better understanding about Security Groups, refer to Understanding Application Security Groups.
Get Service Instance GUID¶
Run cf service INSTANCE_NAME --guid to get the guid of the service instance.
$ cf service my-rabbitmq --guid
ca16f111-5073-40b7-973a-156c75dd3028
Check available Security Groups¶
To see all available security groups use cf security-groups.
$cf security-groups
Getting security groups as demo@anynines.com
OK
Name Organization Space
#0 public_networks
#1 dns
#2 tcp_open
#3 guard_432fb752-876d-443b-a311-a075f4df2237 demonstrations demo
#4 guard_ca16f111-5073-40b7-973a-156c75dd3028 demonstrations demo
There we can see a security group with the name guard_ca16f111-5073-40b7-973a-156c75dd3028 was successfully created.
Note
If the connection between the application and the service instance cannot be established, check if a security group was created.
Backup and Restore Service Instances, Download Backups¶
a9s RabbitMQ provides an easy way to create backups and restore if needed.
Get Dashboard Address, Login and Authorize¶
- Get the dashboard URL with
cf service SERVICE-NAME.$cf service my-rabbitmq Service instance: my-rabbitmq Service: rabbitmq Bound apps: Tags: Plan: rabbitmq-xs Description: This is a service creating and managing dedicated RabbitMQ service instances and clusters, powered by the anynines Service Framework Documentation url: Dashboard: https://a9s-rabbitmq-dashboard.aws.ie.apps.eu1.mindsphere.io/service-instances/ca16f111-5073-40b7-973a-156c75dd3028 Last Operation Status: update succeeded Message: Started: 2017-10-26T08:28:38Z Updated: 2017-10-26T08:28:38Z - Enter the dashboard URL into your browser and authenticate with your WebKey user.
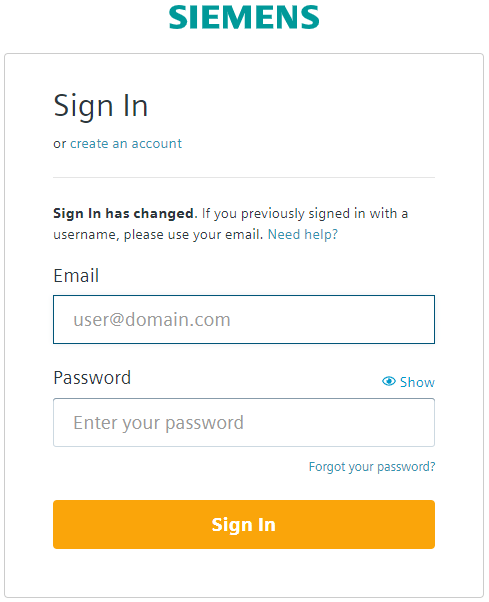
- You will be prompted to enter your login token.

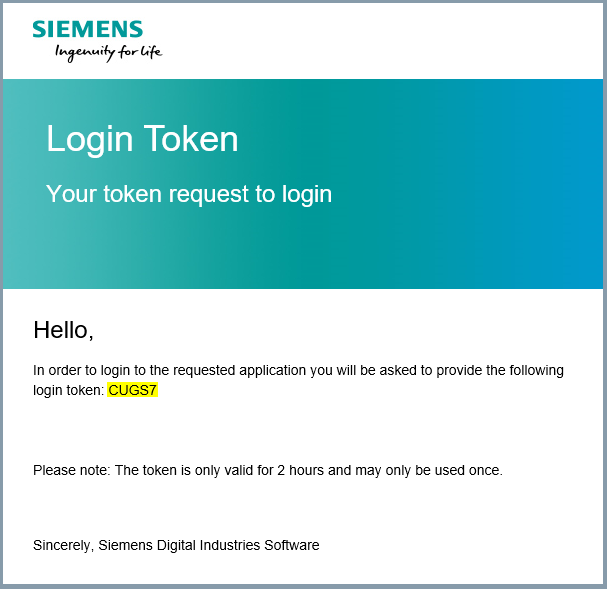
The login token will be sent to you by email. Copy your login token from email and paste it in "Enter login token" field. Click Submit.
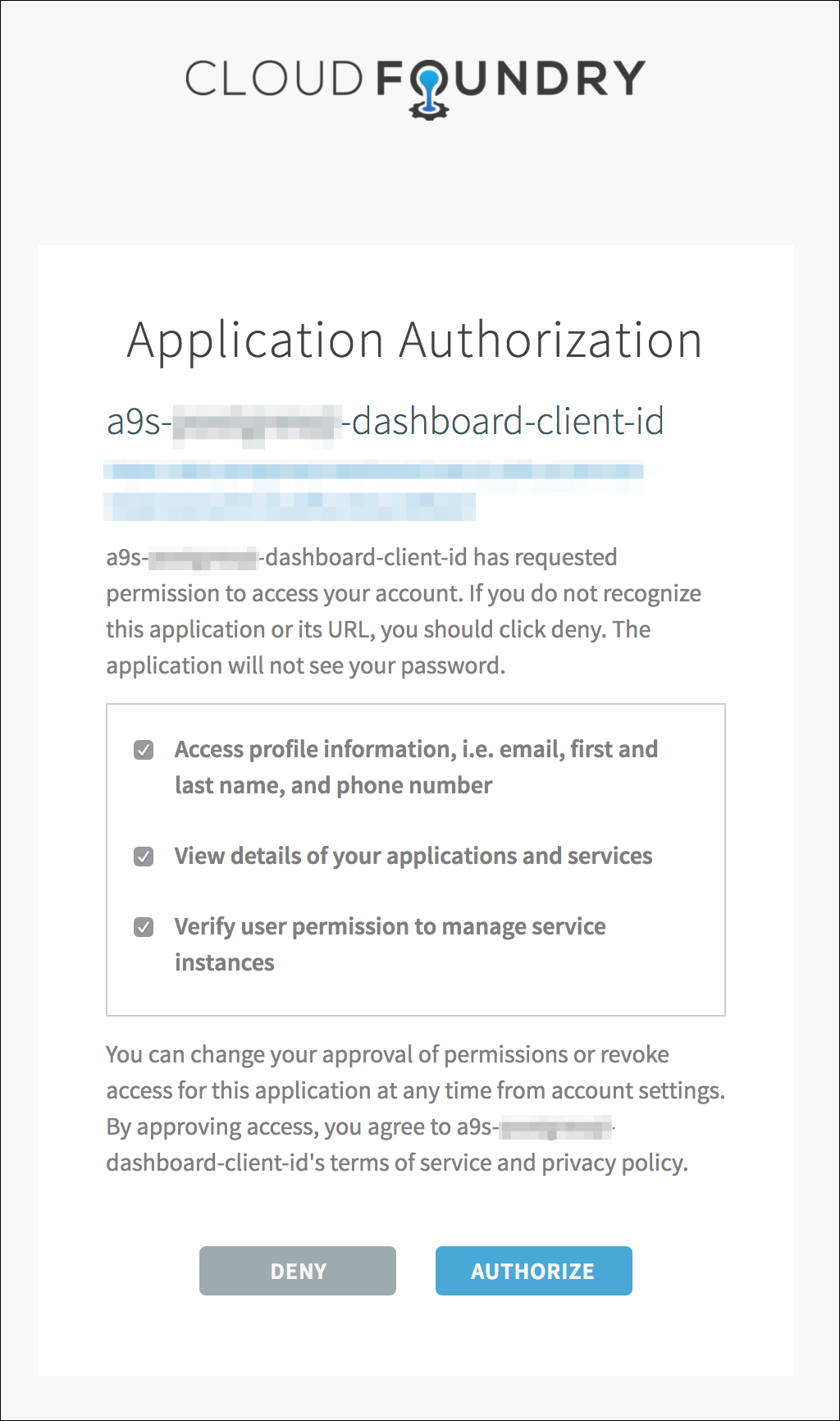
- Click Authorize to approve the authorization request.
Perform a Backup¶
On the dashboard, you can trigger a backup by clicking on the Settings icon and selecting Manually Trigger A Backup.
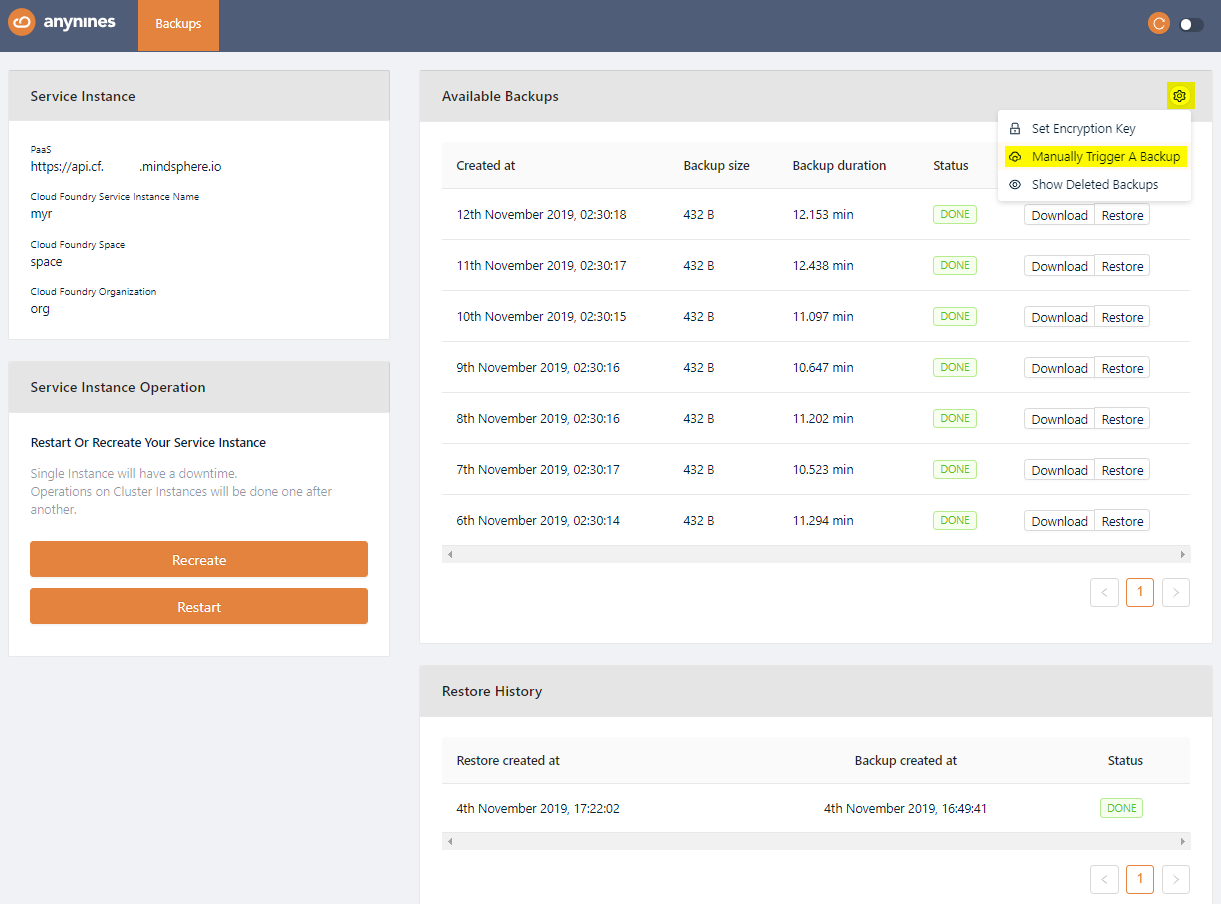
After a short period of time, the backup will be queued. The backup process will start soon.
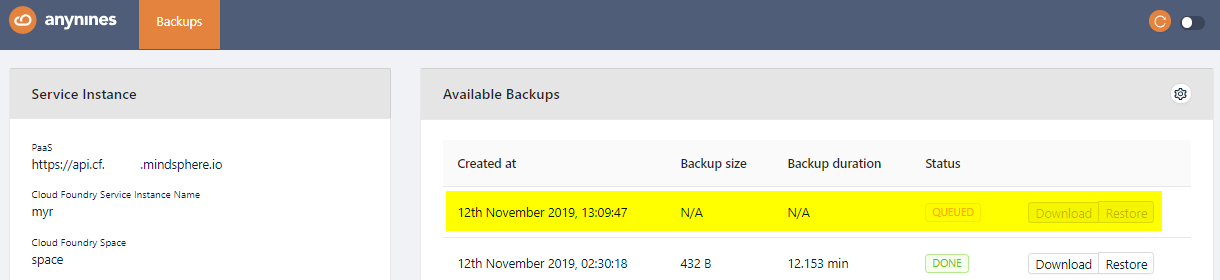
Note
Depending on the size of the data, the backup might take some time.
Restore a Backup¶
Open the dashboard again and select the backup you would like to restore. Click the Restore button of the backup. After a short period of time the restore will be triggered.
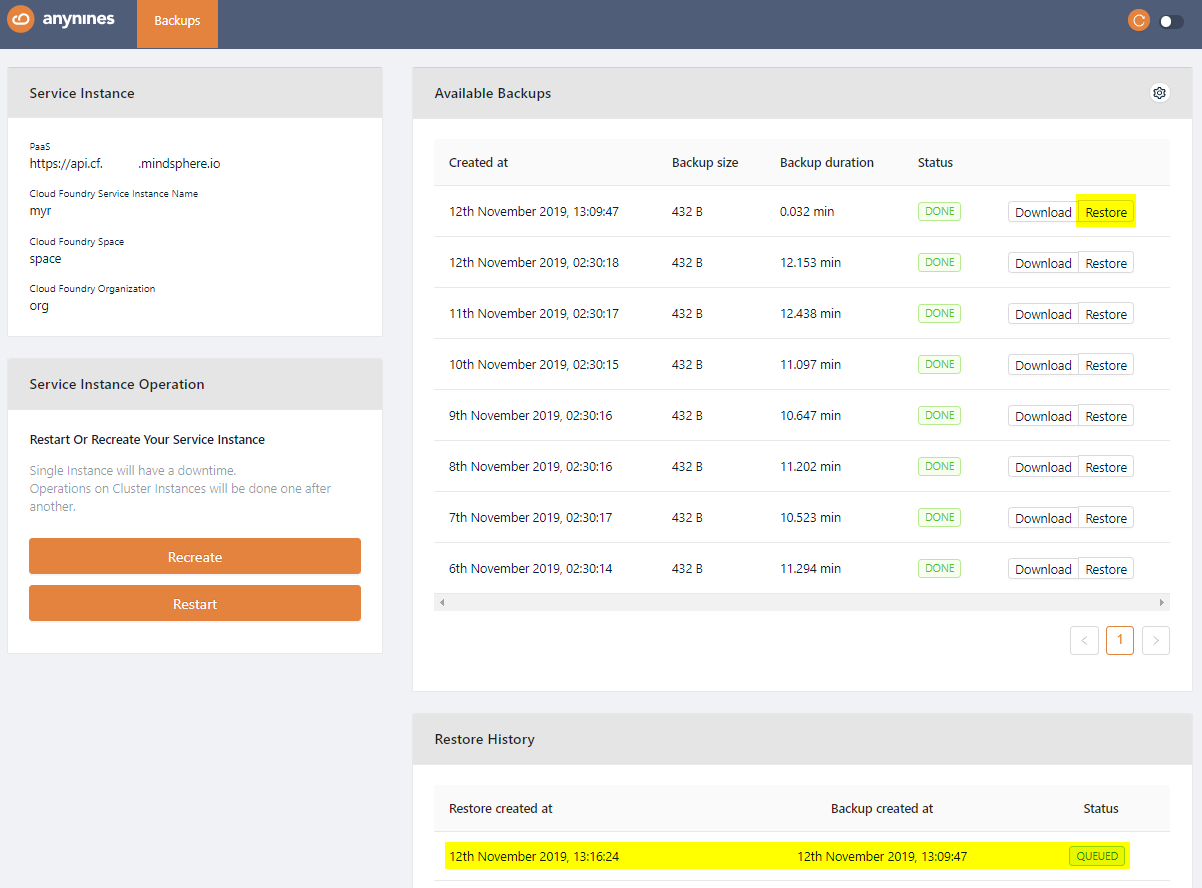
Note
Depending on the size of the data the restore might take some time.
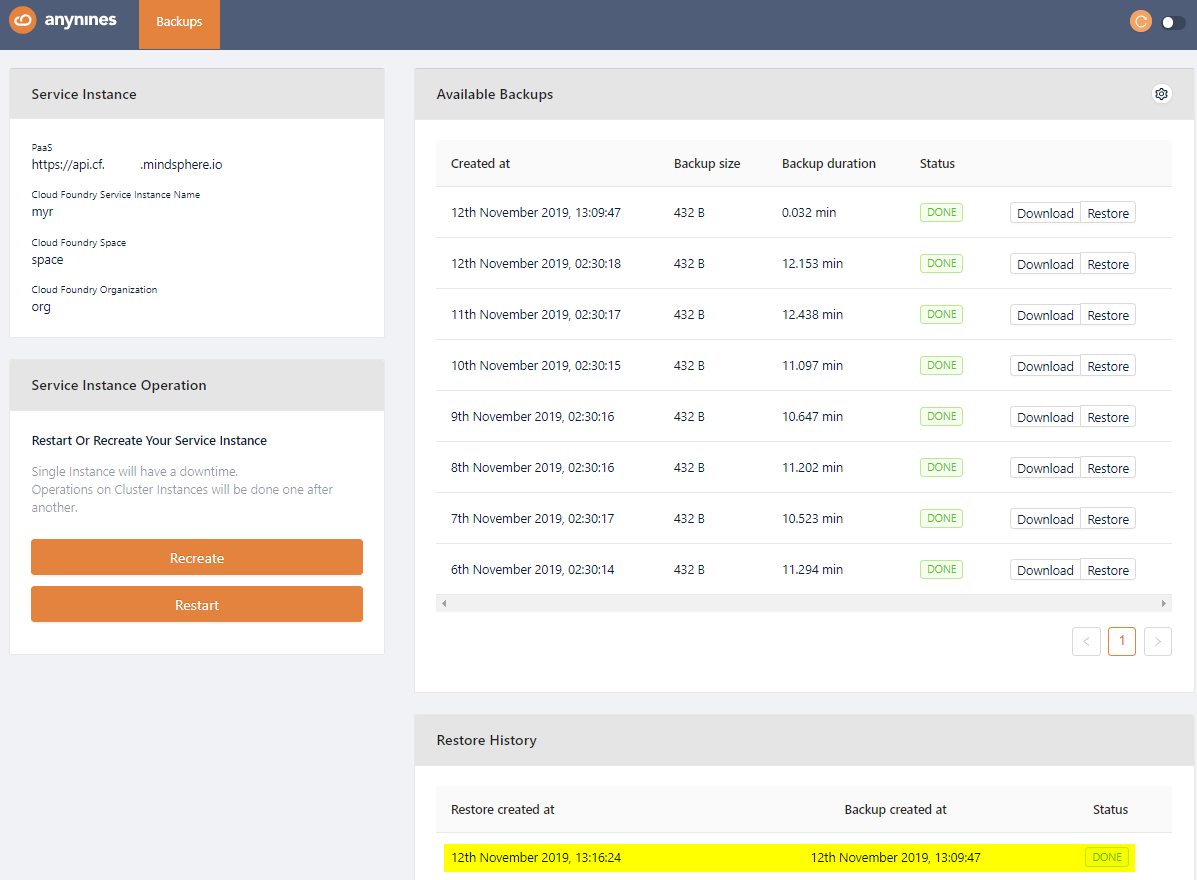
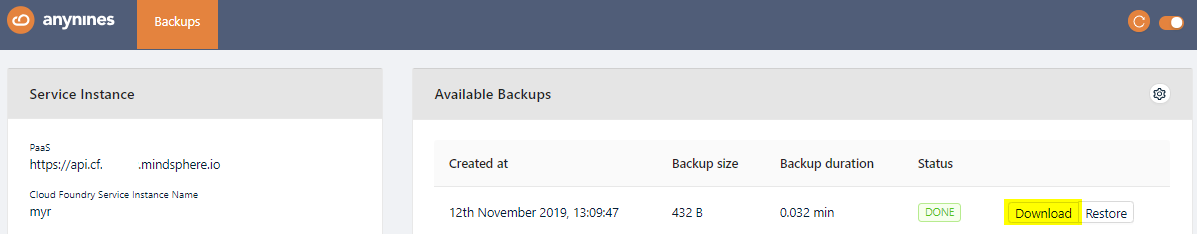
Download a Backup¶
To be able to download a performed backup, you first have to set a personal encryption key. Otherwise a performed backup is not downloadable.
To set a personal encryption key, open the Service Dashboard for the appropriate Service Instance as shown above. Click the Setting icon and Set Encryption Key button.
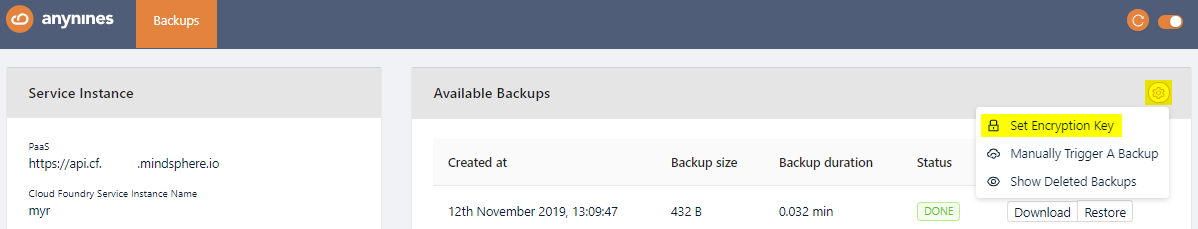
Set the encryption key and click the Save button. The minimum length for the encryption key is 8 characters.

The newly created backup will now show a Download button. Click on this button to download a backup.
Note
If you change your personal encryption key, you will no longer be able to download performed backups encrypted with your old personal encryption key.
Use RabbitMQ Plugins¶
RabbitMQ allows to enable the following RabbitMQ plugins:
- rabbitmq_consistent_hash_exchange
- rabbitmq_federation
- rabbitmq_federation_management
- rabbitmq_mqtt
- rabbitmq_sharding
- rabbitmq_shovel
- rabbitmq_shovel_management
- rabbitmq_stomp
- rabbitmq_tracing
Installation¶
You can install RabbitMQ plugins with the cf create-service and cf update-service commands using additional configuration parameters.
cf create-service rabbitmq36 rabbitmq-xs my-rabbitmq-service -c '{ "plugins": ["rabbitmq_shovel", "rabbitmq_shovel_management"] }'
cf update-service my-rabbitmq-service -c '{ "plugins": ["rabbitmq_shovel", "rabbitmq_shovel_management"] }'
Use RabbitMQ Management Dashboard¶
a9s RabbitMQ has management dashboard support enabled. The dashboard is running on the service instance VM so it is not possible to open the dashboard in your browser directly. CF provides a smart way to create SSH forward tunnels via a pushed application. For more information about this feature see the Accessing Apps with SSH section of the CF documentation.
First of all you must have an application bound to the service. How to do this see Bind an Application to a Service Instance.
Note
cf ssh support must be enabled in the platform. Ask your administrator if you are not sure.
Get Dashboard Url and Credentials¶
When you follow this instructions Obtain Service Instance Access Credentials you will get the hostname of the service and the user credentials.
$ cf env rabbitmq-app
Getting env variables for app rabbitmq-app in org phartz / space develop as admin...
OK
System-Provided:
{
"VCAP_SERVICES": {
"rabbitmq36": [
{
"credentials": {
"host": "d67901c.service.dc1.a9svs",
"username": "brk-usr",
"password": "password",
"port": 5672,
"uri": "amqp://brk-usr:password@d67901c.service.dc1.a9svs:5672"
},
"label": "rabbitmq36",
"name": "myrabbit",
"plan": "rabbitmq-xs",
"provider": null,
"syslog_drain_url": null,
"tags": [
"message broker"
],
"volume_mounts": []
}
]
}
}
Notice the host d67901c.service.dc1.a9svs, the username brk-usr and the password password. You will need this in the next step.
Create Tunnel to The Management Dashboard¶
With the cf ssh as mentioned before you can create a ssh forward tunnel to the management dashboard.
$ cf ssh rabbitmq-app -L 15672:d67901c.service.dc1.a9svs:15672
vcap@956aaf4e-6da9-4f69-4b1d-8e631a403312:~$
Note
Don't forget to close the session with exit.
Log in to The Management Dashboard¶
When the ssh tunnel is open you can access the Dashboard with your Browser at http://localhost:15672.
To log in to the management dashboard you need the user credentials.
Note
For regular access to the management dashboard, the user credentials provided in the environment variables of a bound app are sufficient. You can get these credentials with cf env my-app.
If you need extended access rights, you need to create a service key using the administrator role and log in to the dashboard with the credentials provided in service key. Use cf create-service-key my-rabbitmq my-rabbitmq-key -c '{"roles": ["administrator"]}' to create a service key using administrator role. You can find the credentials in service key with cf service-key my-rabbitmq my-rabbitmq-key.
Extended access rights are also needed for some RabbitMQ plugins like rabbitmq_tracing.
If the login was successful, you should see the dashboard as followed. 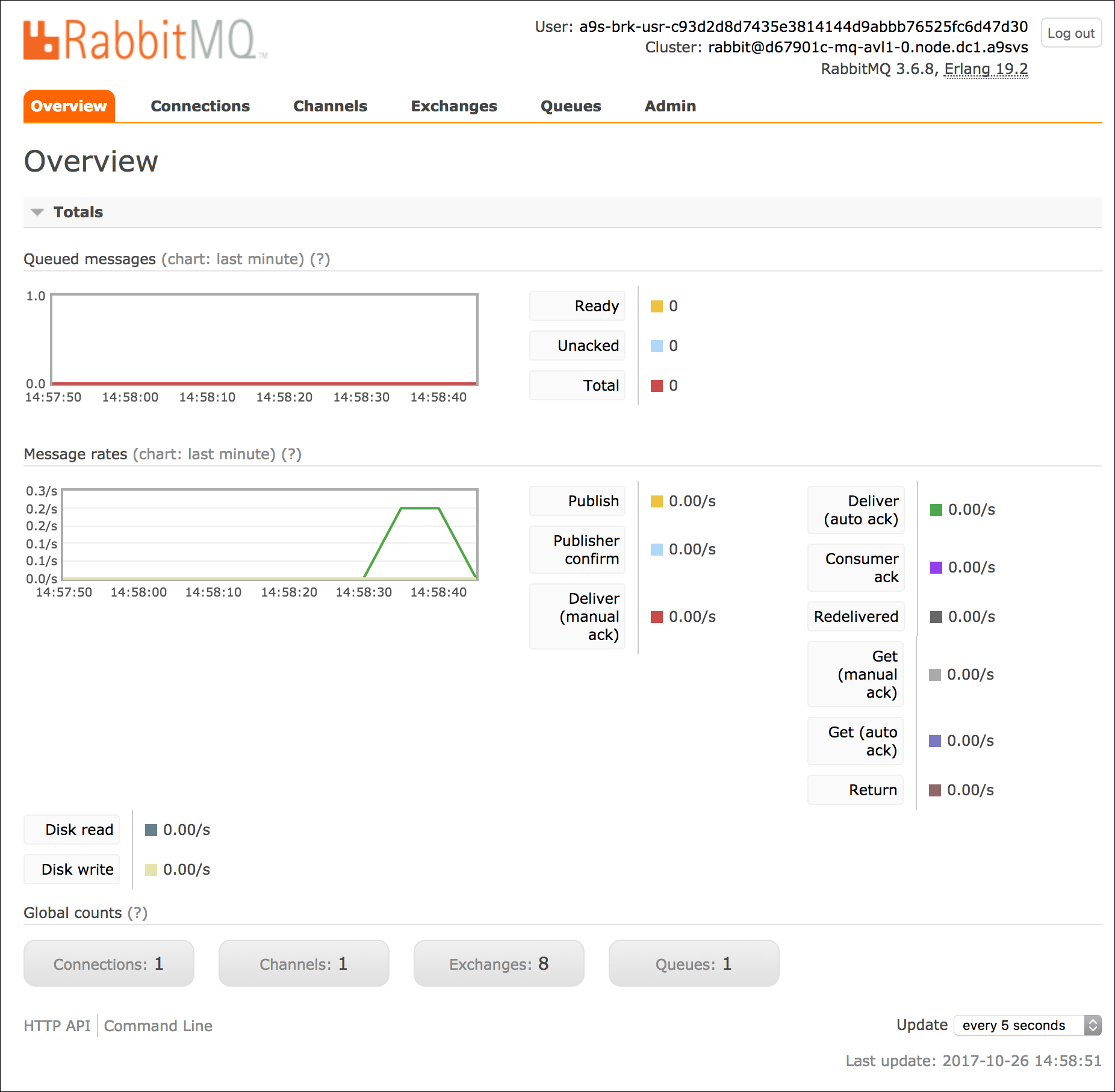
Make a Service Instance Locally Available¶
It is possible to access any of the a9s Data Services locally. That means you can connect with a local client to the service for any purpose such as debbuging. CF provides a smart way to create SSH forward tunnels via a pushed application. For more information about this feature see the Accessing Apps with SSH section of the CF documentation.
First of all you must have an application bound to the service. How to do this see Bind an Application to a Service Instance.
Note
cf ssh support must be enabled in the platform. Ask your administrator if you are not sure.
Get The Service Url and Credentials¶
When you follow this instructions Obtain Service Instance Access Credentials you will get the hostname of the service and the user credentials.
$ cf env rabbitmq-app
Getting env variables for app rabbitmq-app in org test / space test as admin...
OK
System-Provided:
{
"VCAP_SERVICES": {
"rabbitmq": [
{
"credentials": {
"host": [
"d67901c.service.dc1.a9svs"
],
"password": "brk-usr",
"username": "password"
},
"label": "rabbitmq",
"name": "my-rabbitmq-service",
"plan": "rabbitmq-xs"
}
]
}
}
...
Notice the host d67901c.service.dc1.a9svs, the username brk-usr and the password password. You will need this in the next step.
Create a Tunnel to The Service¶
With the cf ssh as mentioned before you can create a ssh forward tunnel to the management dashboard. Use port 9200 to connect to the a9s RabbitMQ Instance.
$ cf ssh rabbitmq-app -L 9200:d67901c.service.dc1.a9svs:9200
vcap@956aaf4e-6da9-4f69-4b1d-8e631a403312:~$
When the ssh tunnel is open you can access the instance over the address localhost:9200.
Note
Don't forget to close the session with exit.
Except where otherwise noted, content on this site is licensed under the Development License Agreement.