Introduction¶
System Manual  ¶
¶
Data Contextualization allows the user to correlate data from multiple sources and generate powerful insights that would not be possible if the data were stored in separate apps. The workflow of Data Contextualization consists of the following steps:
- In the Data Contextualization application, create one or more data sources by constructing Data Registries.
- Add files to Integrated Data Lake, which leads to schema generation for the registry.
- Create SQL query to correlate data from one or more data sources.
- Execute the query and review the query results. The Business Intelligence application in Insights Hub is used to produce dashboards based on query results in Data Contextualization.
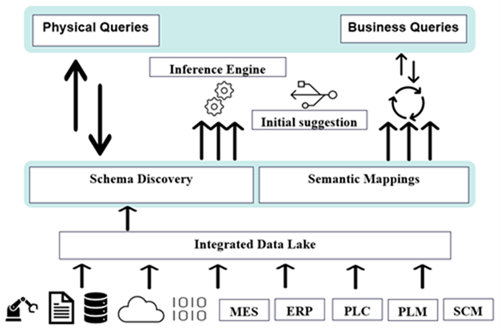
Data Contextualization also allows the user to create a semantic model as an abstraction layer over one or more physical schemas.
A domain expert often creates the semantic model. The user can select multiple configurations to combine the physical tables based on their shared properties as part of the semantic model definition which provides an inference feature using which the user can infer one or more registries or data sources. This also provides an initial suggestion which can be modified while building a semantic model.
A domain expert creates the semantic model. The user can select multiple configurations to combine the physical tables based on their shared properties. In addition, the user can define domain-specific business attributes and relate them to physical schema attributes. The semantic model once generated can be used to write semantic queries using SQL statement.