Identity Management¶
Idea¶
The Identity Management Service manages environments, users and groups within Insights Hub. It enables customers to access the User Accounts and Authentication (UAA) service used within Insights Hub for identity management and authorization.
Access¶
For accessing this service you need to have the respective roles listed in Identity Management roles and scopes.
Basics¶
Environments¶
An environment is an organization-specific logical environment for your data. An environment typically represents a legal entity, such as a company or corporation. Insights Hub is a multi-tenant architecture.
An environment comprises up to two zones for identity management and access control:
-
User zone
Every environment has a user zone. It enables users of the environment to log in and use applications the company has subscribed to. Administrators of the environments can manage the users and assign roles in the user zone to provide users with access to subscribed applications. -
Provider zone
The provider zone represents an additional environment required for web application and API development and operation. Every DevOps plan environment has a provider zone, which stores all information related to access management required for either development or operations (e.g., roles, permissions, applications, technical users).
As environment names are global resources, they must be unique across all environments.
Each user environment needs to define at least one administrator for managing the users and roles.
Users and Groups¶
Every environment has its own users and has roles available depending on the applications it is subscribed to. A role represents a grouping of permissions required to access an application. By modeling roles as SCIM groups, the User and Roles management follows the SCIM standard (System for Cross-domain Identity Management).
Currently, within the user zone, SCIM groups are only used to represent roles.
In addition, SCIM groups may represent user groups (for managing sets of users), data groups (for managing end customer access to data, assets, etc.) and permissions (for managing more fine-grained access to resources, only within provider zone of a environment).
Roles and Scopes¶
The following information is relevant for environments with a provider zone only.
If you expose an API for your web application, scopes define the application specific permissions. Scope names typically reflect these permissions in a syntax like:
{apiName}.{permission/action}
The following list shows examples for the CRUD-permissions of an IoT service:
iot.c(permission to create objects in IoT)iot.r(permission to read objects in IoT)iot.u(permission to update objects in IoT)iot.d(permission to delete objects in IoT)
Scopes are mapped to a specific role. A role name has the following syntax:
mdsp:{tenantName}:{application/apiName}.{roleName/action}
Thus, all scopes above could be mapped to a role called
mdsp:core:iot.admin
Application-specific roles and scopes are defined in provider environments and can be managed within the developer cockpit application. See also HowTo Cloud Foundry application.
OAuth Client¶
The following information is relevant for environments with a provider zone only.
An OAuth client (also called technical user) allows your application to acquire a token to access protected resources without the need of human user interaction. This is necessary for doing regular background activities (batch activities) within your application or if your application is not hosted behind Industrial IoT Gateway and therefore does not receive interactive user tokens in request headers. OAuth clients are defined within the provider zone of your environment and comprise a client ID and client secret, which allow to obtain a token using the client credentials grant (RFC 6749).
Note
The userID for Identity Management API is not the same as the user_id in a decoded token. Instead, a filter with the user's email address needs to be used to get the specific data on a user.
OAuth clients for your provider environment can be acquired as described in the HowTo self-hosted application.
The client secret should be updated before it expires, refer to Client Secret Rotation.
External Group mapping¶
This feature offers automatic assignment or un-assignment of Insights Hub roles to the users based on external groups defined in Identity Provider (IdP). This update happens on every user log-in. This feature is available with API first approach.
To configure this feature, follow the below steps:
- Add external group as additional attribute in IdP config so that external group attribute comes as a claim in IDP ID token. Please refer the sample below.
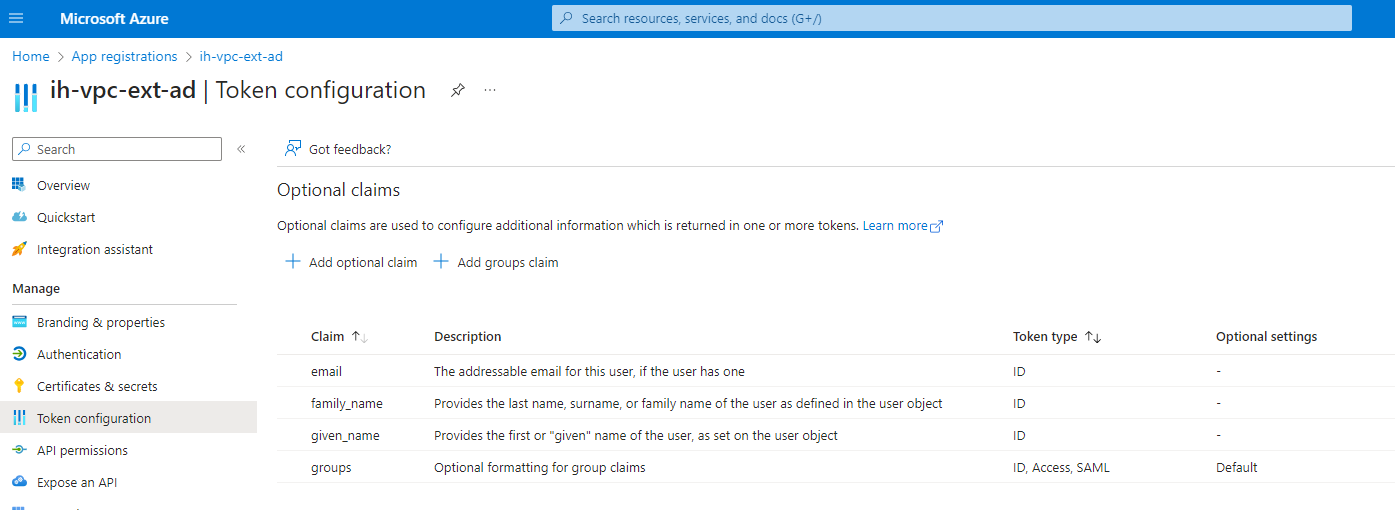
- Define the attribute mapping in Insights Hub IdP configuration using IDP API.
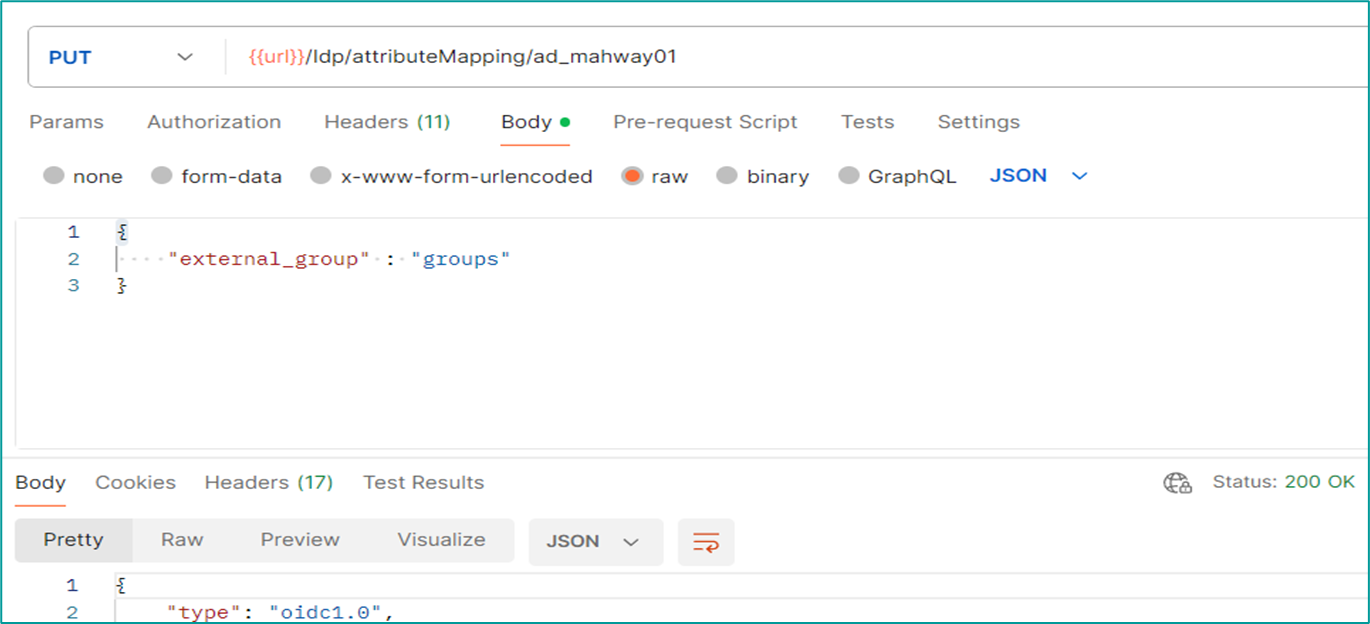
- Create mapping between Insights Hub roles/user group and groups defined in IdP using External Group Mapping API
- After the user logs into Insights Hub, the user automatically gets assigned to Insights Hub role/user group that is mapped with external group in IdP.
Features¶
The Identity Management Service exposes its API for realizing the following tasks:
- List all users of a environment
- Create, get, update, delete users of a environment
- Get all roles assigned to the own user
- List all SCIM groups of the user zone of a environment
- Create, get, update, delete SCIM groups of the user zone of environment
- List, add, remove members of a SCIM group of the user zone of environment
- Create and update mapping for external groups from IdP to Insights Hub roles
Example Scenario¶
The administrator of a brewery wants to prepare the environment for the new developers of their web application.
Use the Identity Management Service to populate the environment with new users and assign them the roles required for development (For example, mdsp:core:StandardUser, mdsp:core:Developer).
Related Links¶
Except where otherwise noted, content on this site is licensed under the Development License Agreement.